 |
Dataflow Software Stack
032db78
Master Thesis of Mathijs Saey at the VUB
|
 |
Dataflow Software Stack
032db78
Master Thesis of Mathijs Saey at the VUB
|
This is the main documentation of the dataflow software stack, created by Mathijs Saey for his thesis at the VUB.
These pages serve a number of purposes:
The main goal of the dataflow software stack was to experiment with a prototypical implementation of a dataflow virtual machine and a compiler that generates input for such a machine. As the name implies, this machine utilizes the the dataflow architecture to achieve a high amount of parallelism. Concretely, our compiler accepts IF1, which it transforms into DIS, a low-level dataflow language. Afterwards, this DIS program can be utilized by DVM to execute our program. Utilizing DIS instead of a more traditional low-level language such as x86 allows us to keep track of the data dependencies in the program on every level of the software stack.
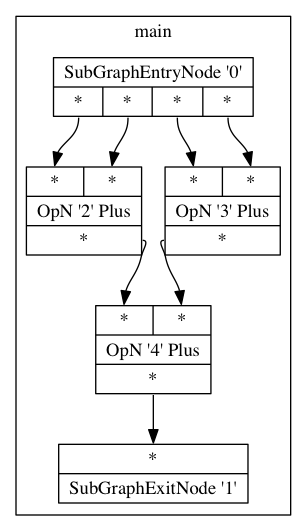
In short, the general idea behind dataflow is that an instruction in the program is executed once it's inputs are ready. This property allows us to exploit the implicit parallelism of programs. A dataflow program can be represented as a graph, in such a graph, nodes represent operations while edges represent data dependencies between these operations.
A visual representation of such a dataflow graph can be seen right of this section. This graph was generated from the following Sisal code.
As we can see, this program simply takes 4 inputs, and adds all of these together. The generated dataflow graph shows us that both of the additions could be carried out in parallel.
Sisal is a language designed to be a high level variant for languages such as PASCAL that can work on multicore machines. During the first compilation phase sisalc (the sisal compiler) compiles Sisal to IF1, an intermediate language, which represents the sisal source code as a dataflow graph.
Our research is focused on the compilation and execution of a dataflow program, and not on the design of a dataflow language. For this reason, we decided to use IF1 as the primary input language of our software stack. Incorporating sisalc offers us a high-level language for writing dataflow programs, along with a compiler that removes the complexity of the language for us.
More information about IF1 along with some sisal and IF1 code samples can be found in the IF1 overview.
Running DVM and DISc is quite trivial at the moment. All you need is a working python interpreter. Man pages for DVM and DISc can be found in the resources folder of the repository.
You need to install sisalc, the sisal C compiler if you want to produce your own IF1 files from sisal source code.
The sites of all these tools and the used versions can be found below:
| Tool | Version | Website |
|---|---|---|
sisalc | 14.1.0 | http://sourceforge.net/projects/sisal/ |
python | 2.7.6 | http://www.python.org/ |
Our stack is split into 2 components.
 1.8.8
1.8.8